#nextjs vs react
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Next.js vs. React: Which Front-End Framework to Choose?
Stuck deciding between Next.js and React for your next project? Both are powerful tools for front-end development, but the right choice depends on your needs. In our latest blog, we break down the key differences, strengths, and use cases of Next.js and React to help you make the best decision. Check out 7Span’s guide to learn which framework aligns with your goals and development style!
0 notes
Text
Next.js Vs React: Why to choose Next.js in 2024
In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, choosing the right backend JavaScript framework is pivotal. Two giants, Next.js and React, dominate the scene. But how do they stack up against each other in 2024? Next.js vs React: Key Comparisons 1. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and Static Site Generation (SSG) Next.js offers built-in support for SSR and SSG, making it a go-to for…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text

How to Use Laravel with React, Vue, or Next.js?
Learn how to build modern, interactive web applications by integrating Laravel with React, Vue, or Next.js
#How to Use Laravel with Vue#laravel next.js#laravel vs nextjs#laravel vs react#How to Use Laravel with Next.js#hire expert laravel developer#hire Laravel Developer
0 notes
Video
youtube
How Mantine UI Can Help You Build Apps 5X Faster | 2025
Looking for the fastest way to build stunning web apps? Mantine UI can help you build apps 5X faster with its powerful, customizable, and developer-friendly components. In this video, we explore why Mantine UI is gaining massive popularity among React developers and how you can use it to speed up your projects.
From ready-to-use components to advanced theming options, Mantine UI is designed for both beginners and pros. Whether you’re creating dashboards, landing pages, or full-scale applications, Mantine UI gives you the flexibility and performance you need.
🔥 Key Highlights: ✔️ What makes Mantine UI unique? ✔️ Hands-on demo of Mantine components. ✔️ How Mantine UI compares to other UI libraries. ✔️ Best practices for seamless UI design.
Don’t miss out—watch now and start building faster with Mantine UI! 🚀
🔔 Subscribe for more web development tips & tricks!
🔥 Hashtags
#MantineUI #ReactJS #WebDevelopment #UIDesign #Frontend #ReactComponents #OpenSource #JavaScript #NextJS #TechTrends
🔑 SEO Tags
Mantine UI, Mantine UI tutorial, Mantine UI React, best React UI library, React UI components, how to use Mantine UI, Mantine UI vs Material UI, Mantine UI vs Chakra UI, best UI library for React, React component library, React UI framework, UI design in React, front-end development, build React apps faster, React UI templates, React theming, responsive UI with Mantine, web development 2025, modern UI frameworks, free React UI components, open-source UI library, Mantine UI review, best UI kit for React, Mantine UI examples, Mantine UI customization, UI/UX with Mantine, front-end tools for developers, how to style React apps, developer productivity tools, speed up UI development, React UI best practices, Mantine UI pros and cons
0 notes
Text
Detailed Comparision NextJS vs Remix: Which One to Choose in 2025?

What’s common in NextJS vs Remix?
Both are popular frameworks built on React. When choosing the right framework for building dynamic websites, Remix and Next.js are the popular choices. They both extend React’s capabilities to build high-performance and SEO-friendly web applications.
Both are React-based frameworks offering different approaches for web app development, meeting modern-age web development needs. Learn how NextJS vs Remix differentiates to help you decide which framework to choose in 2025.
Next.js Overview
17.9% of developers prefer it due to its flexibility, performance, and ease of use. Things to know about Next.js-
React framework introduced by Vercel in 2016
Streamline server-rendered, static websites, and single-page applications (SPAs) development.
Offers features like automatic code splitting, server-side rendering, and static site generation for next-gen dynamic web app development.
Powerful choice for delivering fast, SEO-friendly web experiences
Provide built-in support for TypeScript, CSS-in-JS, API routes
Can be integrated with the Vercel platform for deployment and hosting
Remix Overview
1.6% developers prefer Remix. However, the number is very small compared to Next.js, it is still popular due to its modern and opinionated approach to web development. Things to know about Remix-
It follows a “Fullstack React” approach that improves the developer’s experience through features like server-side rendering, data loading, and routing.
Focuses on structured application architecture and data loading patterns.
Simplify complex tasks like server-side rendering and state management.
Follows the “Routes as Data” concept, where routes are treated as data sources, making it easier to handle data fetching and rendering.
built-in server and client-side hydration mechanisms to ensure fast initial page loads and smooth transitions while minimizing unnecessary reloads.
Key Differences: Remix vs. Next.js
· Remix is as fast as Next.js for serving static content, ensuring a smooth user experience.
· Remix is faster than Next.js at serving dynamic content, avoiding slow loading indicators.
· Remix performs better on slow networks, loading faster on a 3G connection than Next.js.
· Remix automatically handles errors, interruptions, and race conditions, while Next.js does not.
· Next.js encourages client-side JavaScript for dynamic content, whereas Remix doesn’t rely as much on it.
Which React Framework to Choose- NextJS vs Remix?
In the end, the Next.js vs Remix comparison shows that both frameworks are powerful, but each has its own strengths. Next.js is great for developers who want a more structured setup with strong community support and a focus on static and server-side rendering. It’s perfect if you want something that just works out of the box.
On the other hand, Remix is ideal for developers who want more control over things like routing and data loading. It focuses on performance, reliability, and making sure your app works well even in tough conditions (like offline).
By understanding the differences between Next.js and Remix in terms of performance, features, and use cases, you can make a better decision for your project. Both frameworks have clear benefits, and which one you choose depends on what you need and what you’re trying to build.
Original Source of Content: Click Here
#nextjsvsremix#next.jsvsremix#remixvsnext2025#nextvsremix#advantagesofnextjs#nextjstoremix#isremixbetterthannextjs
0 notes
Text
What is Next.js vs Nest.js?

Next.js is a React framework for building server-side rendered and static web applications. Nest.js is a Node.js framework focused on building scalable, maintainable backend applications. While Next.js is for front-end, Nest.js specializes in backend architecture.
For more information read our blog: https://www.bitcot.com/nestjs-vs-nextjs/
0 notes
Text
#mobile app development#software#ui ux development services#web developing company#web development#ai#react#nextjs
0 notes
Text
Nestjs vs Nextjs: A Comprehensive Comparison for Developers

When it comes to web development, selecting the appropriate framework is crucial. Nest.js and Next.js are two prominent frameworks, each catering to different development needs. Let’s delve into their technical aspects to help you decide which is right for your project.
Nest.js is a progressive Node.js framework designed for building efficient, scalable, and maintainable server-side applications. Utilizing TypeScript, Nest.js ensures strong typing and modern JavaScript features, which enhance code quality and developer productivity. Its modular architecture facilitates the organization of code into easily manageable modules, making it ideal for enterprise-level applications. Nest.js supports a variety of libraries and tools, including TypeORM for database management and Passport.js for authentication, making it a robust choice for complex backend systems.
On the flip side, Next.js is a React-based framework perfect for building server-rendered or statically generated web applications. Known for its exceptional SEO capabilities, Next.js offers features like automatic static optimization, dynamic routing, and API routes. Recent advancements in static site generation (SSG) and incremental static regeneration (ISR) enable developers to create high-performance websites that provide excellent user experiences. Next.js also simplifies full-stack development by allowing API routes within the same project.
In conclusion, if your project requires a sophisticated backend with extensive APIs, Nest.js is the optimal choice. For projects emphasizing frontend performance and SEO, Next.js is unparalleled. Explore more about these frameworks and make an informed decision for your next development project on our blog.
Check out our blog for an in-depth comparison of Nest.js and Next.js to determine the best framework for your needs.
1 note
·
View note
Text
ReactJS vs. Next.js: Which is Best for Web Development?

When starting with web development, choosing the right framework can be a bit overwhelming. Let’s break down the basics of ReactJS and Next.js to help you decide which one suits your needs.
What is ReactJS?
ReactJS is a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces, especially single-page applications. It’s maintained by Facebook and a community of developers. Here’s why ReactJS might be the right choice for you:
Component-Based: Build encapsulated components that manage their own state.
Reusable Components: Reuse components to build complex UIs.
Virtual DOM: Efficient updates and rendering of components.
What is Next.js?
Next.js is a React framework that adds more features and functionalities, making it easier to build production-ready applications. It’s developed by Vercel. Here’s why you might consider Next.js:
Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Improve performance and SEO by rendering pages on the server.
Static Site Generation (SSG): Pre-render pages at build time for faster load times.
API Routes: Create backend endpoints without needing a separate server.
Key Differences Between ReactJS and Next.js
Rendering Methods:ReactJS: Client-Side Rendering (CSR) by default.Next.js: Supports SSR, SSG, and CSR.
Routing:ReactJS: Needs a third-party library like React Router.Next.js: Built-in file-based routing.
Development Experience:ReactJS: More control and flexibility; requires more setup.Next.js: Out-of-the-box features for a smoother development experience.
When to Use ReactJS?
You need a highly interactive UI: Perfect for dynamic, single-page applications.
You want full control over your setup: Great if you enjoy customizing your development environment.
You’re working on a smaller project: Easier to manage without the overhead of a full framework.
When to Use Next.js?
SEO is crucial: SSR and SSG improve search engine rankings.
You want faster load times: Static generation helps with performance.
You prefer an all-in-one solution: Built-in routing and API handling streamline development.
Conclusion
Choosing between ReactJS and Next.js depends on your project needs. For a dynamic, highly interactive application with custom setups, ReactJS is ideal. For a fast, SEO-friendly, and production-ready app, Next.js is the way to go.
Looking for a reliable partner to bring your Web Development vision to life? Look no further than Inwizards Software Technology! Our expert team specializes in creating dynamic, responsive, and scalable web solutions tailored to your business needs. Whether you need a sleek website, a robust e-commerce platform, or a custom web application, we’ve got you covered.
Let’s transform your ideas into reality. Contact Inwizards Software Technology today and take the first step towards digital excellence!
Visit our website to learn more and get in touch with us: Inwizards Software Technology
Read our blog — https://www.inwizards.com/blog/nextjs-vs-reactjs/
#ReactJS and Next.js#inwizards software technology#web development company#web development services#web development
0 notes
Text
ReactJS vs NextJS: Which Framework Should You Choose in 2025?

Two web application development frameworks that jump in one's thoughts are ReactJS & NextJS. Each has its own advantages and has been adopted by many developers all around the world. This blog post will discuss the debate of ReactJS vs NextJS so you can better determine what fits your project needs. Let's go over each framework, look at their features, and then see how to choose between them.
Understanding ReactJS
A library developed by Facebook (now Meta) with a focus on making user interfaces has attracted much attention since its release. React is lightweight, efficient, and reusable, making it one of the most popular libraries in the industry today. With React, you can create dynamic user interfaces by breaking down complex components into smaller, reusable parts, which are easy to manage and can be used repeatedly in different parts of the application.
Key Features of ReactJS
Component-Based Architecture: React JS utilizes a component-based structure, and developers can create encapsulated components that maintain their own state. This way modularity is improved and code reuse increases.
Virtual DOM: The virtual DOM of React optimizes the rendering of the UI, reducing duplicate updates. Thus, this makes the React-based applications faster and interactive.
Strong Community Support: You have a large number of developers for the ReactJS solution; thus, it is easy to find resources, tools, or a development company that focuses on ReactJS.
ReactJS is great if you are more interested in more interactive UIs, or want maximum flexibility in structuring your web application. This is particularly ideal if building a single-page application that doesn't necessarily benefit from server-side rendering.
Introduction to NextJS
NextJS is a React framework that is developed by Vercel. It expands on top of everything that is possible inside of React to offer more tools and conventions, especially around server-side and static site generation. The combination brings ease of use within React with scalability in server-side rendering, so faster page loads and good SEO are achieved. While ReactJS is strictly only about client-side code, NextJS is born to ease full-stack development by handling both client- and server-side code.
NextJS: Important Features
Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Server-side rendering is made much more elegant using NextJS. It ensures that the initial page load is faster, and all the optimistic outputs in terms of SEO.
Static Site Generation (SSG): It has worked more towards static websites and loads faster if it is enabled during the build time. It's on NextJS.
API Routes: You can set API routes right within the application; this does not complicate the idea of backend integration of NextJS.
File-Based Routing: NextJs works on file-based routing. This makes the structure and navigation of projects much easier.
NextJs can be a solution to all those applications which might require server-side rendering or static site generation. In addition, it is suitable for large applications in cases of routes with some complexity.
ReactJS vs NextJS: Major Differences
Although reactjs vs nextjs have so many advantages, the choice between them is still basically project-specific. Now, let's dive into the major differences of the nextjs vs reactjs debate:
1. Rendering Capabilities
ReactJS primarily depends on client-side rendering, which is perfect for SPAs but somehow faces issues with load time and SEO.
Since NextJS is integrated with SSR as well as SSG, it is very suitable for SEO-based sites and e-commerce applications.
2. Routing
In the case of ReactJS library, it does not include any built-in routing. You are going to be dependent upon another library for the routes creation as in the case of React Router.
With regards to NextJS, file-based routing is bundled in the package and therefore it provides you easier and simple handling and configuration of routes.
3. Learning Curve and Flexibility
ReactJS is much, much more flexible so you could turn it into anything you'd like. It's pretty difficult and a pain to work with if you don't know the best practices.
There is more convention set in place in NextJS, which means it's a bit less flexible but very straightforward in the learning path for beginners.
SEO and Performance
The general trend for ReactJS is that it is optimized to get fast performance on client-side rendering but lacks SEO.
It is all about SEO and performance since it supports options for SSR.
When to Use ReactJS
If it's about almost building a complex user interface where SEO matters less, then ReactJS would be the best. It's ideal for highly complex point-to-point interfaces, dashboards, etc., requiring efficient state management and user engagement.
ReactJS is much more flexible, and, in the final end, one of the go-to choices for the developers who wish to have an overall structure for their applications. Along with this, the community comprises a humongous amount of people who can provide a company for ReactJS Development or support.
When to Use NextJS
NextJS is suitable for projects where performance and SEO are at number one. Server-side rendering and static site generation make an ideal application that has good architecture for performance as well as proper SEO. E-commerce sites, content-driven websites, and high complex applications with client- and server-side logic may gain more with NextJS.
Moreover, if your team is a noob towards React, NextJS can benefit them in the development process as well. Considering all of these benefits of having full-stack possibilities nowadays, several NextJS Development Company specialize only in RectJS.
Which Framework Should You Choose: ReactJS or NextJS?
When to choose one of the following frameworks, ReactJS & NextJS- it solely depends upon the needs of your project:
If you are looking for the most flexibilities, and you would love to keep focus more on client-side rendering, but with complete ignorance towards SEO, then ReactJS would be a better option.
However, if you are going to pay most heed to SEO, you need better loading times, or you want to have a mix of server-side and client-side development, then NextJS will be at the top choice.
Summarizing it all, the nextjs vs reactjs choice is not exactly which one is better, but what best suits your goals. Both ReactJS Vs NextJS are strong tools and have their own share of strengths. In case it is for a single page application, static site, or web application that has SEO as well, you will surely find both ReactJS & NextJS fitting the bill.
Final Thoughts
ReactJS & NextJS has changed the face of web development wherein it has made things easier and faster to build high-performance applications with much ease. And whether you are considering to use either ReactJS & NextJS, never forget to remember the requirements of your project, familiarity of your team with the tools available and your scope. By getting the right framework, your application is sure to be built up to its potential, scalable and user-friendly.
Right ReactJS Development Company can make a difference between being adequately guided and fully equipped in that walk you have planned on taking on in the pursuit of development.
0 notes
Text
JAMstack, Headless CMS vs Traditional CMS
This article will cover the basics of what a headless CMS actually is. You will learn about the main differences between a headless CMS (eg. Storyblok, Contentful, Prismic, …) - and more traditional CMS like Adobe Experience Manager, Wordpress, and Sitecore.

What is a headless CMS?
A headless CMS is a back-end only content management system (CMS) built from the ground up as a content repository that makes content accessible via a RESTful API for display on any device.
The term “headless” comes from the concept of chopping the “head” (the front end, i.e. the website) off the “body” (the back end, i.e. the content repository). A headless CMS remains with an interface to add content and a RESTful API (JSON, XML) to deliver content wherever you need it. Due to this approach, a headless CMS does not care about how and where your content gets displayed. A headless CMS has only one focus: storing and delivering structured content.
The counterpart of a headless CMS is often called monolithic, regular or coupled CMS and we’re going to use those terms later on.

Let’s have a look at WordPress and their feature set:
A database for the content to read and write to.
An admin interface to let editors manage the content.
An integration of reading and writing.
The actual front-end that combines the data from the database with HTML.
To convert that into a headless CMS we simply remove the feature four from the stack. The head of that CMS - the actual website - was simply chopped off. What still stays is an application that allows content management (Admin UI) and reading (API: combined Integrations). Voila you now have got yourself a headless CMS.

Other than by using a regular/monolithic CMS, one website can’t be built only with a headless CMS. A headless CMS separated the head from its stack and therefore lacks this point by design. Therefore, the developer must craft the website by his- or herself and use the Content Delivery API of the headless CMS to load the content.
Creating the whole website on their own seems like a big task on the list, but by decoupling the CMS from the front-end a developer can choose any technology they are already familiar with and do not need to learn the technology for that specific CMS. Another big bonus is the fact that one developer can also focus on their own work without handling the bugs of an already existing stack of technology - therefore it is easier to optimize pages for googles pagespeed and even relaunch parts of the website without needing to care about the content.
Do I need a headless CMS?
The answer to this question is quite simple, but it won’t help you much: It depends on your requirements. There are use cases where one CMS outstands the other and vice versa. To help you decide, let’s have a look at the benefits really quick:
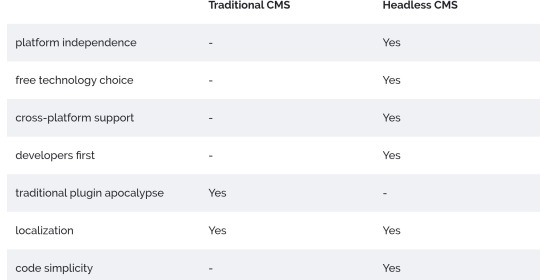
Use cases for Headless CMS
Build a website with a technology you are familiar with.
Websites, Web apps that use JavaScript frameworks (VueJs, React, Angular)
Websites created with static site generators (Jekyll, Middleman, …)
Native Mobile Apps (iOS, Android, Windows Phone)
Enrich product information on ecommerce sites.
Point is: It is not limited to websites
A headless CMS can deliver your content through an API directly to where you need it. Because of the headless approach the content can be used on an iOS app, Android app as well as any platform and technology you can think of (yes and even a Windows Phone App) and is therefore a powerful option for mobile and web developers.
Many believes JAMstack, PROGRESSIVE WEB APPS, Static Site Generators and Headless CMS are the future!
During the start of the age of the internet, static site were prevalent. You had to know how to write HTML to be called a Web Developer. Back then WordPress didn’t exist. All you had was HTML, CSS and JavaScript, eventually WordPress came and promised a clean interface, no coding skills need and a whole lot of themes/templates which you could edit by yourself through their interface. Since then wordpress has pretty much become an internet ruler along side Google. But now the tide is shifting, will you shift as well.
What is a JAMstack
You can also use JAMstack with headless CMS. The JAMstack allows people to create websites that are simpler, faster, and more secure than other web development methods. Sites created with the JAMstack are delivered by pre-rendering files that are served directly from a CDN, removing the requirement to manage or run web servers.
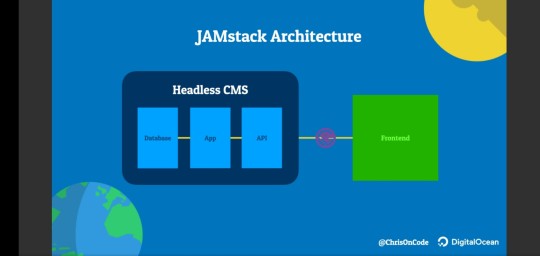
You may have already seen or worked on a JAMstack site! They do not have to include all attributes of JavaScript, APIs, and Markup. They might be built using by hand, or with Jekyll, Hugo, Nuxt, Next, Gatsby, or another static site generator…
The thing that they all have in common is that they don’t depend on a web server.
JAVASCRIPT
Any dynamic programming during the request/response cycle is handled by JavaScript, running entirely on the client. This could be any front end framework, library, or even vanilla JavaScript. eg Jekyll, Gatsby, Nuxtjs, Nextjs, Hugo, Hexo, Vuejs.
API
All server-side processes or database actions are abstracted into reusable APIs, accessed over HTTPS with JavaScript. These can be custom-built or leverage third-party services. eg GitHub API PI, Vero API, Google sheets API, YouTube API.
MARKUP
Templated markup should be pre-built at deploy time, usually using a site generator for content sites, or a build tool for web apps.
When is your site not built with the JAMstack?
Any project that relies on a tight coupling between client and server is not built with the JAMstack. This would include:
A single page app that uses isomorphic rendering to build views on the server at run time.
A monolithic server-run web app that relies on Ruby, Node, or another backend language.
A site built with a server-side CMS like WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, or Squarespace.
Why choose JAMstack?
Better performance – Why wait for pages to build on the fly when you can generate them at deploy time? When it comes to minimizing the time to first byte, nothing beats pre-built files served over a CDN.
Higher Security – With server-side processes abstracted into microservice APIs, surface areas for attacks are reduced. You can also leverage the domain expertise of specialist third-party services. And also with server side CMS you get a larger surface area prone to attack.
Affordable, Easier Scaling – When your deployment amounts to a stack of files that can be served anywhere, scaling is a matter of serving those files in more places. CDNs are perfect for this, and often include scaling in all of their plans.
Better Developer Experience – Loose coupling and separation of controls allow for more targeted development and debugging, and the expanding selection of CMS options for site generators remove the need to maintain a separate stack for content and marketing.
#references : StoryBlok https://www.storyblok.com/tp/headless-cms-explained?_ampify=1&__twitter_impression=true
1 note
·
View note
Text
Next.js vs React: Why Choose Next.js For Web Development
Are you ready to elevate your web development game? Discover why Next.js is the go-to framework for modern, efficient, and user-friendly web applications. On the other hand, React native helps to create robust and interactive user interface. Here's a quick rundown of its standout features:
🔄 Routing Made Easy: With dynamic, nested, and index routing, Next.js simplifies navigation and page rendering, reducing code duplication and maintenance.
⚡ Advanced Rendering: Server-side rendering (SSR) enhances SEO and user experience by delivering fully rendered HTML content quickly. Plus, client-side rendering ensures dynamic interactions.
🔍 Efficient Data Fetching: Use getStaticProps and getServerSideProps for optimized performance. Fetch data seamlessly from databases, APIs, and more, ensuring your app stays dynamic and up-to-date.
🎨 Flexible Styling: Choose your preferred styling methods, from CSS modules to Tailwind CSS and CSS-in-JS, for a seamless design process.
🔧 Comprehensive Optimization: Enhance your app’s Core Web Vitals with optimized images, fonts, and scripts.
🔤 TypeScript Support: Enjoy better type checking and efficient compilation with custom TypeScript plugins. 👉 Next.js revolution - the latest sensation reshaping the future of web development! Know more: https://www.softwebsolutions.com/resources/nextjs-vs-react.html
Next.js isn’t just a framework; it’s a game-changer. From improved SEO to enhanced performance and accessibility, it's the toolkit every developer needs. Ready to make the switch?
0 notes
Text

What to choose React or NeXT.JS for full stack development? Know about Serverside rendering, routing and performance optimization. https://bit.ly/react-vs-nextjs
0 notes
Video
youtube
React vs Next js Which Should You Learn for Upcoming Projects
React vs Next js Which Should You Learn for Upcoming Projects
https://youtu.be/Kd_Mdr42c-0
Welcome, In this video, we'll be exploring the differences between React and Next.js, and helping you decide which one to learn for your upcoming web development projects. With the React official team recently recommending Next.js for certain use cases, it's important to understand the benefits and tradeoffs of each technology.
We'll start by providing an overview of React and Next.js, and discussing their respective strengths and weaknesses. We'll cover topics like server-side rendering, performance, scalability, and SEO, and explain how each technology approaches these areas.
Finally, we'll wrap up with some tips on how to get started learning React or Next.js, and some resources for further exploration. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, this video will help you make an informed decision on which technology to learn for your upcoming projects.
==============TIMELINE================
0:00 - Introduction to React and NextJS
0:12 - Comparison between React and JavaScript
0:40 - Brief history of React and NextJS
1:20 - How it started?
4:13 - Reasons why you should learn React before NextJS
5:30 - Situations where NextJS may be the better option
6:50 - What to do if you have doubts?
#projects #webdevelopment #developer #javascript #react #technology #team #learning #help #seo #like #video #scalability #next.js #reaCT
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Nextjs vs Nodejs: Which Backend Framework to Choose in 2025
Today, businesses rely on interactive and dynamic web applications to improve their online presence. One of the most popularly used backend technologies is JavaScript which not only creates real-time web apps but also helps developers improve their coding experience.
As of 14 June 2024, nearly 98.8% of websites use JavaScript.
63.61% of developers use JavaScript for client-side and server-side app development.
Global brands (Google, YouTube, Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, etc.) use JavaScript to develop compelling websites.
JavaScript offers several frameworks for efficient developer experience.
Choosing the right JavaScript framework is a strategic decision for overall success. Two popular backend JavaScript frameworks are- Next.js vs. Node.js.
However, Node.js is a runtime environment that runs JavaScript code outside the browser. And Next.js is a React-based framework for building dynamic and hybrid applications. Both offer unique benefits and are suitable for different use cases.
To build modern-age applications, developers must understand where both technologies differ and which one to choose in 2025.
What is Node.js?
GitHub- 108k+ stars, 3500+ contributors
40.8% of backend developers prefer Node.js to build high-end, dynamic, and real-time applications. Since 2009, Node.js has evolved with a strong community improving it over the years.

Source
Here are a few things that you must know about Node.js.
A runtime environment that executes JavaScript on the server side.
Built on Chrome's V8 engine, which is the main reason behind Node.js’s high-speed and efficient applications.
Can handle many concurrent connections.
Has npm (Node Package Manager)- a set of libraries and tools for extended functionalities.
Works well for data-intensive applications that need quick responses.
Supports both vertical and horizontal scaling to meet growing demand.
Easily integrates with JSON for seamless data exchange.
Supported on most platforms, including Linux, Windows, Unix, macOS, and more.
Key Features
Here are some key features of Node.js

Source
Event-driven, asynchronous, non-blocking I/O Model- allows Node.js to handle many concurrent connections efficiently. It also manages resources and I/O operations asynchronously. It means the system will process other requests without waiting for the response from a slower I/O process. It improves the app’s performance and responsiveness. It makes Node.js apps highly scalable.
Modular design- Node.js modular design allows developers to share and reuse code, significantly reducing development time and improving the developer’s experience.
Compatibility across platforms- you can use Node.js across platforms like Mac OS X, Linux, and Windows. It helps developers create a single codebase and deploy it across platforms ensuring the same functionality and responsiveness.
Built-in debugging tools- one of the most prominent features is its built-in debugging tools, allowing developers to identify and fix issues instantly.
NPM (Node Package Manager)- it comes with Nodejs installation. It is a package manager that allows developers to access millions of packages to add more functionalities to a simple app. You can simply install a package for any functionality and use it within your app without developing it from scratch.
Built on Chrome’s V8 engine- it is the reason that Node.js is extremely powerful, efficient, and fast, allowing faster execution of JS code while handling heavy applications with great ease.
Benefits of Using Node.js for Your Business
High performance- Node.js can handle multiple concurrent requests without consuming many resources, making it suitable for developing applications that require high performance and scalability. The V8 engine improves performance and response time. PayPal reduced its response time by 35% using Node.js.
Improves developer's experience- with Node.js, developers can easily use the programming language (JavaScript) to create both backend and frontend. It means developers do not have to switch to another language and frameworks. Node.js has a large ecosystem that allows developers to create a wider range of applications, improving developer’s experience.
Cost-efficient development- Node.js can save up to 58% of development costs. As it can handle many requests at the same time, it requires less resources. It lets you reuse the code, reducing time-to-market and development expenses. This is why, Node.js has become the go-to option for businesses that need cost-efficient yet powerful modern-age solutions.
Growing community- since 2009, Node.js has grown with strong community support. This community has contributed towards Node.js improvements, making it a better technology to meet modern-age development needs. As a developer, you will find packages and libraries to stay ahead by incorporating the latest trends in web app development.
Easy deployment and hosting- Node.js makes it easy to deploy applications on cloud platforms like Heroku, AWS, and Azure. These services simplify the deployment process, allowing businesses to scale their apps as their user base grows. With hosting providers tailored for Node.js, companies can install and manage their apps with minimal setup and maintenance.
Disadvantages of Node.js
Performance bottleneck- Node.js is great at handling many requests at once. But the challenge is, that it uses a single thread to process tasks, impacting performance when dealing with complex calculations. These tasks can create a "bottleneck," slowing down the entire system.
Limited support for databases- Node.js was first created to work with web apps, which meant it didn't support many databases except for MongoDB. It might find it difficult to use Node.js with other types of databases or in different kinds of applications. It limits its flexibility in some cases.
Callback hell- Node.js uses asynchronous tasks and callbacks, but this can make the code messy and hard to follow, especially in complex apps. When callbacks are nested too many times, it creates a "callback hell," that is difficult to manage.
Memory leaks- Node.js relies on a garbage collector to manage memory, but sometimes has memory leaks. It means they don't release memory properly, resulting in performance issues and making the app unstable.
Despite its challenges, top brands like LinkedIn, eBay, Netflix, GoDaddy, Groupon, Uber, NASA, and Walmart, use Node.js for seamless experiences. Today. More than 1 million websites use Node.js.

Source
What is Next.js?
GitHub- 127k stars and 3500+ contributors.
As a new technology in the market, Next.js has gained much popularity since 2017. 17.9% of developers prefer it. Unlike Node.js, Next.js is a React-based server-side rendering framework.

Source
Here are a few things you must know about Next.js.
Developed by Vercel
Open-source framework
Used for creating server-side rendered (SSR) apps and static site generation (SSG) web apps
Based on the principle of “Build once, runs everywhere”
Offers unique features like route pre-fetching and automatic code splitting
built on top of React and runs on top of Node
Offers tools and features for building high-performance, scalable, and optimized web applications.
Improves developer's experience to build fast and efficient web applications
Features of Next.js
Here are some key features of Next.js.
App Directory (New File System Routing)- The new App directory introduces a new file-based routing system, which offers better flexibility and improved server-side rendering (SSR). It allows developers to organize components and pages more efficiently and to define layouts that are shared across different pages. This feature is part of the move towards a more modular and composable approach to building applications.
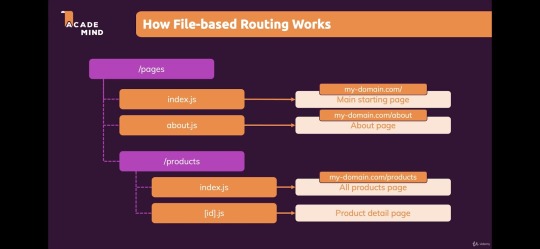
Source
React Server Components (RSC)- it allows developers to render some parts of the app on the server and send only the required HTML to the client. This results in faster page loads and better SEO, as the server can handle complex logic. Server components allow for a more optimized rendering process, minimizing the amount of JavaScript sent to the client.
Automatic code splitting- Next.js automatically splits your code into smaller parts, so only the necessary CSS and JavaScript files are loaded for each page. This makes the files smaller and helps the page load faster. As a result, developers can build fast and efficient web apps with Next.js.
Edge Functions & Middleware- Edge Functions are small, fast-running server-side functions deployed closer to the user on the edge network, improving performance, especially for globally distributed applications. Middleware runs on the edgel, allowing developers to handle tasks like authentication, redirects, and A/B testing with low latency.

Source
Image Optimization Enhancements- it automatically optimizes images based on the user's device and network conditions. The latest updates have improved performance and flexibility in how images are handled, with automatic WebP conversion and better support for blur-up effects.
Hybrid Rendering- With Next.js, developers can use different types of rendering approaches- SSR (server-side rendering), SSG (static site generation), and CSR (client-side rendering) within a single app for optimizing performance, SEO, and user experience.
API Routes- Next.js allows you to create backend API endpoints directly within the project, enabling full-stack development without needing a separate server. This makes building complex applications easier by simplifying data fetching, processing, and handling.
Better SEO and Head Management- Head Management improvements in Next.js allow developers to control meta tags, titles, and other important SEO elements more efficiently. This helps in improving SEO by making the meta tags dynamic and context-specific.
Webpack 5 Support- Next.js now fully integrates Webpack 5, offering better build performance, improved caching, and support for the latest JavaScript features, resulting in faster builds and smaller bundle sizes.
Turbopack (Alpha)- Turbopack is a new bundler from the creators of Next.js, designed to replace Webpack. It's faster and more efficient, especially for large projects. Currently, in alpha, it promises significantly faster build times and hot module reloading (HMR).
Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)- This allows developers to update static pages without rebuilding the entire app, ensuring up-to-date content without impacting the speed of static generation.
Benefits of using Next.js

Source
Improved SEO- Next.js can generate fully rendered HTML on the server using Server-Side Rendering (SSR). This means pages load faster and search engines can easily read and rank them. With Static Site Generation (SSG), pages are pre-built as static HTML during the build, making them even faster and better for SEO.
Blazing fast speed and performance- Next.js has helped streaming app Twitch to reduce its initial load time by 50%. It uses many features like SSR, SGR, and automatic code splitting to load pages quickly and offer a smooth user experience.
Accessibility- due to SSR, web apps have more accessibility. Users can use a reader screen to access the web page content easily.
Improved developer’s experience- Next.js features like a flexible and powerful routing system, an optimized build system, and a large ecosystem of resources, tools, and libraries, lead to the developer’s productivity and experience to build more robust apps.
Enhanced security- as Next.js SSG pre-generates the content and serves the static HTML file. It reduces the risk of security vulnerabilities and attacks.
Disadvantages of Next.js
Complexity- Next.js has many powerful features, but setting it up can be tricky, especially for new developers. It might take longer to get started and configure everything, which can slow down development.
Browser Compatibility- Next.js uses modern JavaScript, which may not work well with older web browsers. Developers need to make sure their app works on the browsers their users are likely to use.
Dependency on React- Next.js is built on React, so you need to understand React well to use Next.js effectively. If you're new to React, this can be challenging.
Next.js can be used to build many different types of projects, such as:
Complex Web Applications
Web Platforms
Multi-Market Solutions
Advanced eCommerce and Retail Platforms
SaaS Products
Interactive User Interfaces
This is why brands like Nike, Hulu, Binance, Twitch, TikTok, and Vercel use Next.js for better performance.
Next.js vs. Node.js: Detailed Comparision
Here is a detailed Next.js vs Node.js comparison.
1. Next.js vs Node.js performance
Web Performance is necessary to keep users engaged. About 40% of online users tend to leave a website that takes longer than three seconds to load.
Node.js is a suitable option for building fast apps as it can handle many tasks at once. It uses an event-driven system, meaning it doesn’t get “stuck” waiting for things to happen. To make your code even faster, you can write asynchronous code that lets multiple tasks run at the same time. Node.js also helps you store and retrieve data efficiently and can avoid issues like memory leaks. Tools like caching and content delivery networks (CDNs) improve load times by serving files closer to users. For high-traffic apps, load balancing spreads the work across multiple servers.
Next.js is a framework built on top of React that makes websites even faster. It has built-in tools for improving performance, like lazy loading images and loading pages in the background for smoother transitions. It also lets you control SEO elements like page metadata, helping search engines understand your content better.
For large apps, Next.js provides monitoring tools to track performance and identify issues before they cause problems. It also includes a bundle analyzer to help you reduce the size of your app and send only the necessary data to the browser. By using CDNs to serve static files, Next.js helps further speed up your site.
2. Next.js vs Node.js scalability
Scalability in web apps means making sure your app can handle many users at once without slowing down or costing too much. It’s about increasing app performance as more people use it, without using too many resources. However, scalability differs from response time—your app can handle many requests but still take longer to respond, or it can respond quickly but struggle with heavy traffic.
In Node.js, scalability challenges include serving files, scheduling tasks, and using resources effectively. To solve these:
Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network) like CloudFront to serve files faster.
For repeating tasks, use a task scheduler like Agenda.js instead of basic timers.
Use Node.js clustering to divide the work between multiple processes, improving performance without overloading.
For Next.js, scalability is achieved by:
Caching: Use CDNs for static content, server-side caching for dynamic content, and client-side caching for API calls.
Load Balancing: Spread user traffic across multiple servers to avoid overloading.
Optimizing Databases: Use techniques like indexing, query optimization, and caching to reduce database load.
Auto-Scaling: Set up your app to automatically add or remove server instances based on traffic or usage.
3. Node.js vs Next.js: Development Speed
Node.js provides a basic platform to build server-side applications using JavaScript. You have to set up a lot of things manually, like routing, handling requests, and serving static files. This means you have more flexibility, but takes more time to set up and develop the app from scratch.
Next.js: It is a framework built on top of Node.js and React. It offers many built-in features like server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), routing, and image optimization. These features make development faster because a lot of common tasks are already handled for you. You don’t have to set up everything from scratch, so you can focus more on building the app itself.
Next.js is faster for development because it provides ready-made tools and features, while Node.js gives you more flexibility but requires more setup.
4. Node.js or Next.js for frontend
Node.js: Node.js is mainly used for backend development, meaning it runs on the server to handle things like saving data to a database, managing user logins, and processing API requests. While it can be used to build parts of the front end (like rendering web pages on the server), it's not specifically designed for that purpose.
Next.js: Next.js is a framework built on top of React and is specifically designed for front-end development. It helps you build fast websites with features like server-side rendering (SSR) and static site generation (SSG). These features make websites faster and better for SEO (search engine optimization). Next.js also makes it easier to manage routing (pages) and other common frontend tasks.
If you're building a website's frontend (what users see and interact with), Next.js is the better choice because it’s made for that. Node.js is mostly for backend work, but it can help with some frontend tasks if needed.
5. Routing
Routing is like a map for your website. When a user asks for a specific page (like by typing a URL), routing decides where the request should go and what should be shown in response. It helps direct the user's request to the right place in your application.
There are two main ways to handle routing in Node.js: with a framework or without one.
With a Framework (like Express.js): Express is the most popular framework in Node.js for routing. It makes things easier by giving you a set of tools to handle routing quickly. You can use methods to define routes (like /home or /about), and each route can have a function that runs when someone visits that page. For example, if someone goes to /home, the app will show the homepage content.
Without a Framework: If you don't use a framework, you have to build your own server and routing system. You'll manually handle the URLs and decide what happens when a user visits different pages.
Next.js Routing: In Next.js, routing is simpler. It uses a file-based routing system. This means that every file you put in the pages folder automatically becomes a route. For example, if you create a file called about.js, Next.js will automatically link it to /about on your website. This system also handles dynamic pages, where parts of the URL can change based on data, like showing a user’s profile page based on their ID.
6. Developers experience
Developer experience (DX) is about how easy and enjoyable it is for developers to work with tools and technologies. If tools are good, developers can build things faster and with fewer problems.
Node.js and Next.js both focus on improving the developer experience in different ways:
Node.js: Node.js lets developers create anything they need, but it can be a bit complex at first. It has NPM, a huge library of tools and packages, making it easy to find solutions for problems. While it’s flexible, beginners might find it tricky until they get used to it.
Next.js: Next.js is simpler and more ready-to-use. It helps build fast websites with features like SEO-friendly pages and easy routing. It does a lot of the work for you, so you don’t have to set things up manually. It’s great for developers who want to build apps quickly without dealing with too many details.
When to Use: Next.js vs. Node.js
Use Next.js when:
E-commerce Websites: Real-time updates, fast performance, and SEO optimization.
Marketing Websites: Highly optimized for fast loading and SEO to attract visitors.
Portfolio Sites: Ideal for showcasing projects and personal portfolios with great performance.
Blogs: Use for content-heavy websites with SEO and fast page loads.
Entertainment & News Apps: Perfect for media-heavy applications with incremental static generation.
Community-driven Websites: Platforms with user-generated content (e.g., forums, social media).
Booking Apps: Websites that require fast interactions and real-time data updates.
Documentation Sites: Ideal for creating fast, SEO-friendly, and easy-to-update documentation.
Information Hubs: Centralized websites for information aggregation and display.
Auction Sites: Real-time data and quick updates, perfect for online auctions.
Minimum Viable Products (MVPs): Quickly build and deploy scalable MVPs with Next.js.
SaaS Platforms: Create fast, scalable, and SEO-friendly SaaS products.
Data Dashboards: Build real-time, data-driven dashboards with fast performance.
Web Portals: For user management, data access, and real-time updates.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Build fast, offline-capable applications for mobile and desktop.
Use Node.js when:
Backend Services: Build and manage server-side applications, APIs, and databases.
Microservices: Create modular and scalable backend architectures for large applications.
APIs: Develop robust RESTful or GraphQL APIs for web and mobile apps.
Real-time Applications: Ideal for building collaborative platforms (e.g., Google Docs), message applications, streaming services, and online gaming apps.
Big Data Analytics: Handle large-scale data processing and analysis.
Wireless Connectivity: Power IoT devices and manage communication with wireless systems.
Web Scraping: Extract data from websites for analytics or aggregation.
Command Line Tools: Create custom CLI tools for automating tasks.
Single-Page Applications (SPA): Build fast and dynamic SPAs using Node.js for backend services.
Internet of Things (IoT): Use Node.js to connect and manage IoT devices and sensors efficiently.
Conclusion
As highlighted earlier, both Node.js and Next.js bring distinct advantages to web development. Next.js, built on React, stands out as a powerful alternative to Node.js for developing fast, dynamic applications. It offers a complete toolset with easy setup, routing, and an enhanced developer experience.
In contrast, Node.js serves as a runtime environment designed for building scalable, real-time applications using an event-driven, non-blocking model. When used together, Node.js and Next.js enable the creation of full-stack web applications, with JavaScript at the heart of the development process.
The choice is completely requirement-based. To build powerful Node.js web applications, connect with a leading app development company. OnGraph sets out to deliver advanced solutions by staying ahead of trends to meet modern-age requirements.
Connect with our experts to make highly performance web apps.
Content Source URL: Check Here
#Next.jsvsNode.js#Node.jsvsNext.jsperformance#Next.jscomparisonwithNode.js#Whichisbetter#Next.jsorNodeJS?#DoesNext.jsreplaceNodeJS?#Isnext.jsfrontendorbackend?#WillNodeJSbediscontinued?
0 notes